WAND
A Wireless and Artifact-Free 128-Channel Neuromodulation Device for Closed-Loop Stimulation and Recording in Non-Human Primates
Closed-loop neuromodulation systems aim to treat a variety of neurological conditions by delivering and adjusting therapeutic electrical stimulation in response to a patient’s neural state, recorded in real time. Existing systems are limited by low channel counts, lack of algorithmic flexibility, and the distortion of recorded signals by large and persistent stimulation artifacts. We address these issues with a wireless artifact-free neuromodulation device (WAND) [1], [2] that enables research applications requiring high-throughput data streaming, low-latency biosignal processing, and simultaneous sensing and stimulation.
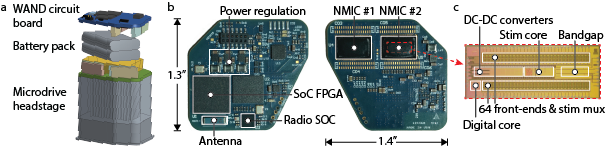
The device is an integrated and non-modular version of OMNI (see OMNI project) [4] with all its components (CM, AM, and two NMs) on a single board, enabling in-vivo expermients of the system. It is capable of closed-loop recording and stimulation on 128 channels, with on-board processing to fully cancel stimulation artifacts. In addition, it can detect neural biomarkers and automatically adjust stimulation parameters in closed-loop mode.

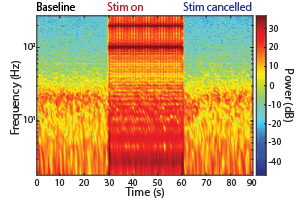
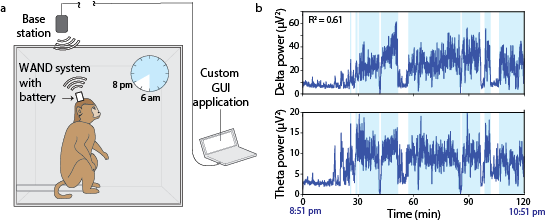
In a behaving nonhuman primate, the device enabled long-term recordings of local field potentials and the real-time cancellation of stimulation artifacts, as well as closed-loop stimulation to disrupt movement preparatory activity during a delayed-reach task. The neuromodulation device may help advance neuroscientific discovery and preclinical investigations of stimulation-based therapeutic interventions.

This project was a collaboration between several groups at UC Berkeley (Profs. Jan Rabaey, Elad Alon, Jose Carmena, and Rikky Muller) and Cortera Neurotechnologies.
-
WAND: A 128-channel, closed-loop, Wireless Artifact-free Neuromodulation Device In Society for Neuroscience (SfN) annual meeting 2017 [PDF]
-
An implantable 700 \muW 64-channel neuromodulation IC for simultaneous recording and stimulation with rapid artifact recovery In Symposium on VLSI Circuits 2017 [PDF]
-
Powering and Communication for OMNI: A Distributed and Modular Closed-Loop Neuromodulation Device In International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) 2016 [PDF]